River and Estuary Observation Network (REON)
History
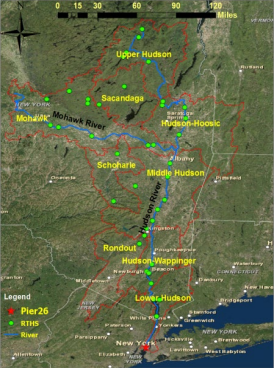
The River and Estuary Observatory Network (REON) was in 2008 by RATES and Clarkson University (Potsdam, NY) and originally comprised several seasonal moored profiling platforms and four year-round Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers (ADCPs) deployed in the Hudson River watershed and interfaced to a Real-Time Hydrologic Station (RTHS). Profilers were used for specific projects; for example, to monitor water quality during dredging of PCB contaminated sediments in Fort Edward, NY; while ADCPs produced a continuous record of 3-dimensional water current throughout the water column. From 2012-2015, with funding from the Dormitory Authority of the State of New York (DASNY), the network was expanded to a total of 40 RTHS stations, where each station included a baseline sensor suite for monitoring water level, precipitation, and assorted meteorological parameters. As of 2022, REON has further expanded to include the IRON network in northern New York State as well as stations in southern Texas for multiple programs including: Texas General Land Office (TGLO) Coastal Management Program, TCEQ CWA-Section 319, and Texas Water Development Board-Freshwater Flows, . An additional 44 REON RTHS stations will be implemented in the Rio Grande Valley as part of a regional Texas Water Development Board-Flood Infrastructure Fund project.
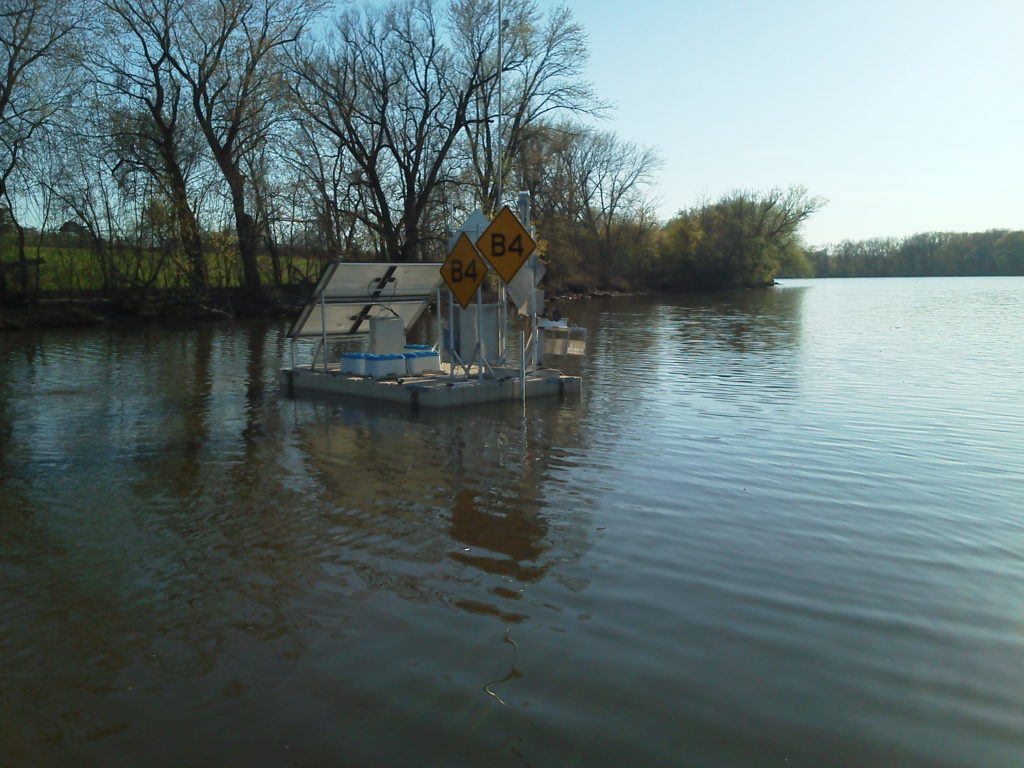
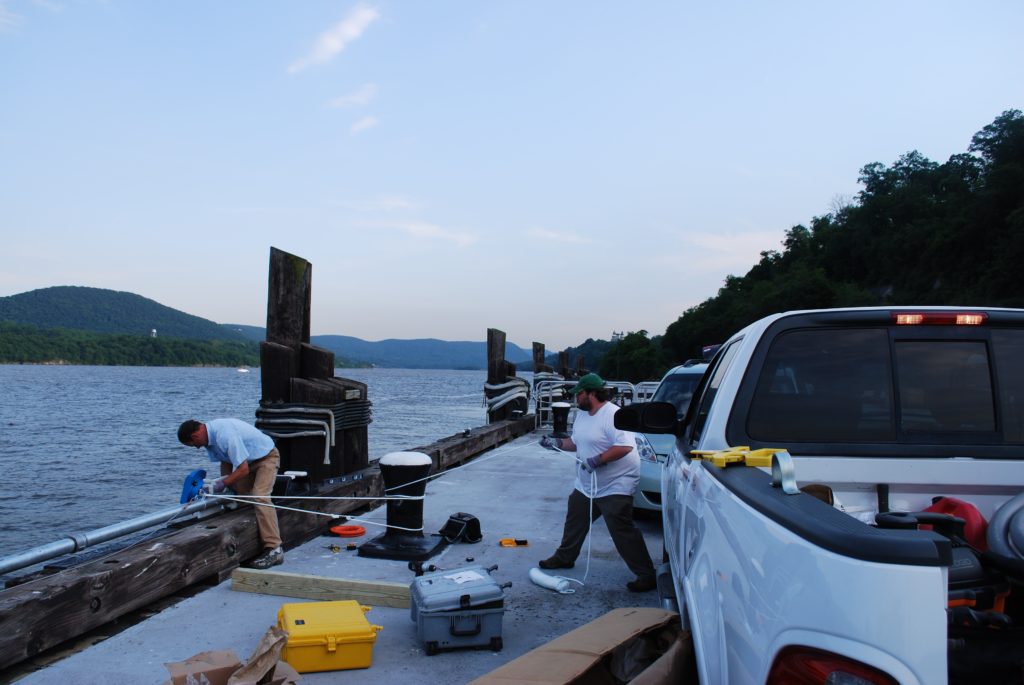



Sensor Technology
REON RTHS platforms have been interfaced with an assortment of sensing equipment, including both commercially purchased instrumentation and custom-designed sensors developed by RATES personnel and affiliates, for the collection, storage, and dissemination of continuous, near-real-time data. Examples include:
- Teledyne-RDI Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers
- SeaBird Conductivity/Depth/Temperature Sensors
- WetLabs FL3 Fluorometers
- YSI EXO2 Multiparameter Sonde
- Sequoia LISSTs
- Aanderaa oxygen sensors
- In-Situ depth sensors and multiparameter sondes
- Assorted meteorological sensors
- Custom-designed depth/stage/temperature sensors
- Custom-designed turbidimeters
- Custom-designed multiparameter sondes
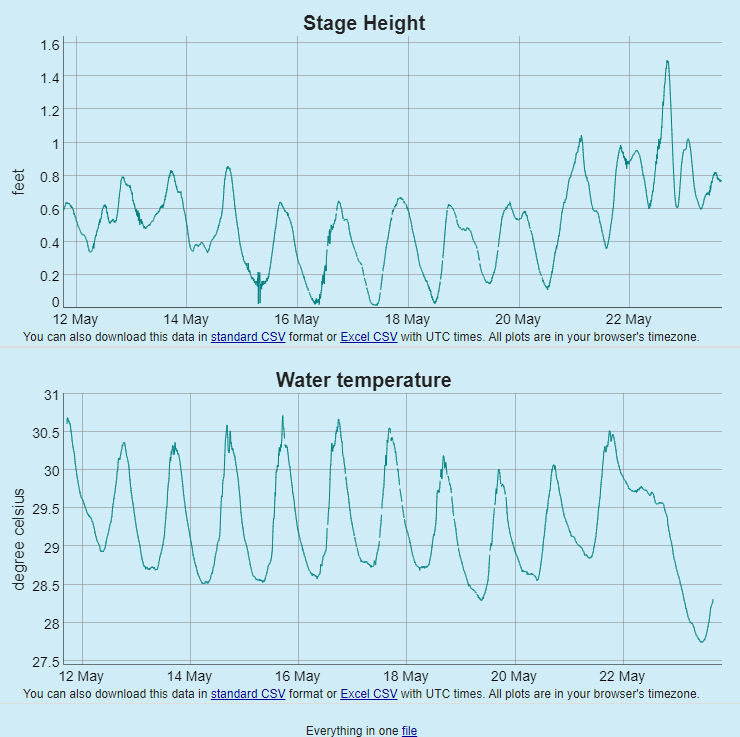
RTHS stations are designed to support deployments of environmental sensor suites for long-term deployments with near real time telemetry of web accessible databases.. RATES also deploys similar systems for high resolution data collection ; for example, conducting river transects with ADCPs to obtain discharge measurements and 3-dimensional current profiles. RATES also designs procedures and support systems for efficient maintenance and quality control of RTHS-reported data.
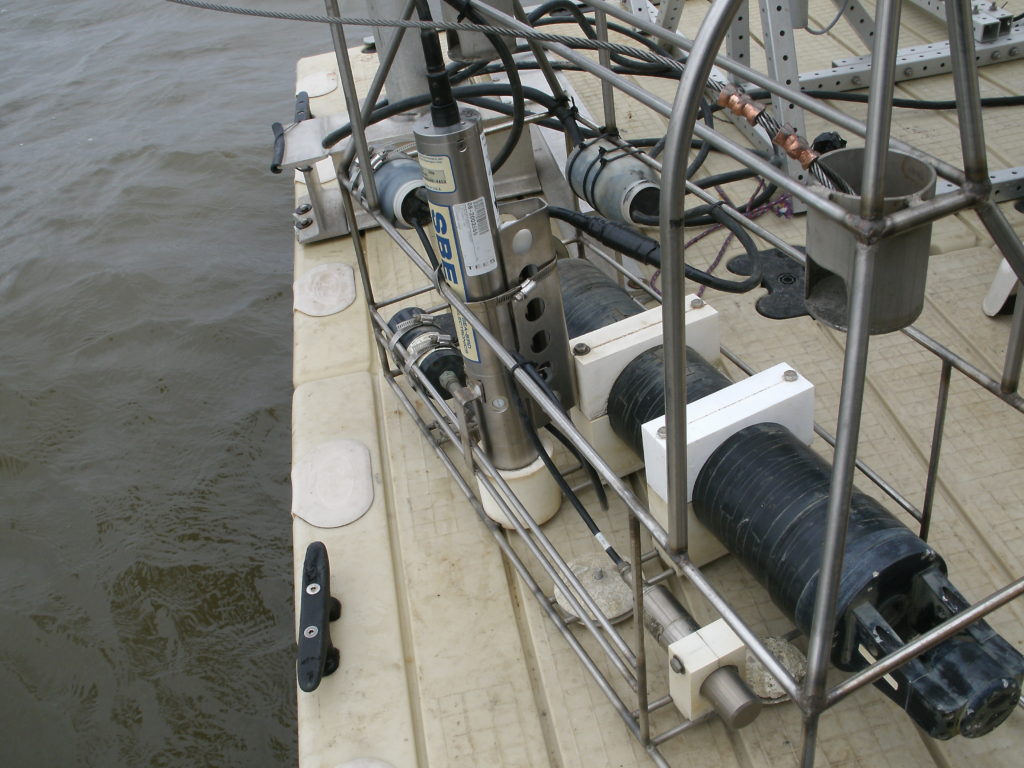




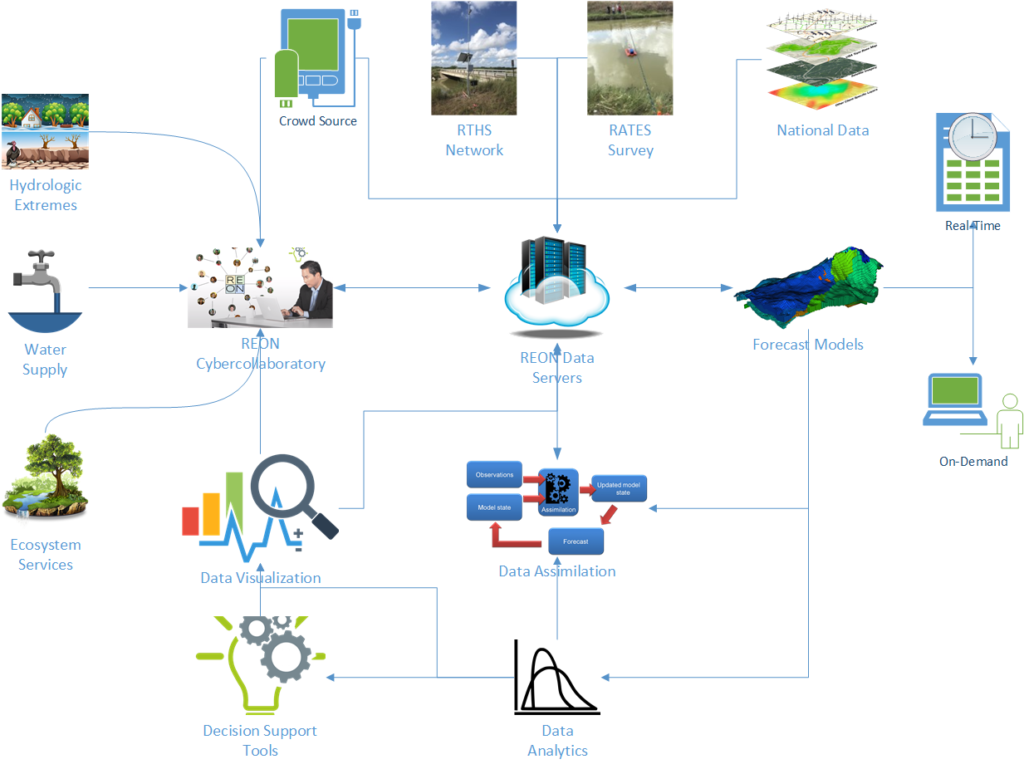
Cyber Infrastructure
Data collected at RTHS platforms are processed and stored in databases for: dissemination to users; assimilation into model applications; network management; and quality control, via the RATES cyberinfrastructure (CI). The two major components are the rths.us data management system and the REON.cc user interface. Additional user interfaces built on REON.cc, such as RGVFlood.com, have been created to serve the needs of particular regions or clients. These systems are continuously evolving and expanding, for ever-improving cost-effectiveness of data collection and management and for an ever-expanding suite of applications utilizing the data.